It’s time to cut out the middleman. Why would we pay an agency that connects users and service providers if we can use an app that directly connects two parts and doesn’t charge fees? People were looking for a way to achieve this and came up with decentralized applications (dApps) that bring specific changes. They promise a digital revolution. Fantastic, isn’t it?
Allow us to spill the tea in the following lines and share all the vital information about decentralized apps and their implementation. You’ll love it and probably want to install one of the applications as soon as possible, or even be the one who creates them and takes all the glory.
If you decide to go one step further and dare to make more significant changes in your life, get ready to build a Polygon dApp with Dev3. You’ll be shocked when you realize that everything is solved in only 15 minutes.
What are dApps?
dApps is an abbreviation for decentralized applications. They are like apps we already use. The only difference is that they are based on a peer-to-peer network like blockchain and use a smart contract.
A third party can’t control them, which is why they are decentralized. With apps like Instagram, Facebook, and Twitter, you must provide personal information if you want to use the apps. But with decentralized apps, that’s not the case.
They can be developed to be used in gaming, finance, storage, streaming, and social media. The protection of user privacy, the absence of censorship, and the freedom of creation are advantages of dApps.
It’s predicted that the future will replace all centralized apps with decentralized ones. All this is packed into one terrific story, slowly getting its epilogue and enticing an increasing number of users to try one of the apps. The good thing we mentioned at the beginning is that within the Dev3 platform, you can create a decentralized app. Today, we will focus on building the Polygon dApp.
What Is Polygon?
Polygon, formerly known as the MATIC network, is a protocol for creating and joining Ethereum-compatible blockchain networks. Its core element is the Polygon SDK, a commutable, customizable framework that encourages the creation of different apps.
Polygon MATIC was first presented in 2017 as a testnet network and later turned into a mainnet. It supports Web3 and the development of dApps. It’s a decentralized Ethereum scaling platform that lets developers create user-friendly dApps with low transaction costs without compromising security.
Polygon is a cross-chain scalability solution that provides the infrastructure to create interconnectable blockchain networks. It plans to bring the scalability and flexibility of sub-chains together with Ethereum’s interoperability, security, and liquidity. It has become popular due to the high permeability and low gas costs that clients and developers experience on its platform.
Ethereum is still the most famous blockchain network. Nonetheless, the use of Ethereum results in high costs, with exchange fees oftentimes costing more than the transferred amount. It’s because Ethereum is utilized by a large number of customers, which leads to reducing the scalability of the exchange.
In such cases, Polygon MATIC is brought into play to solve the problem. The Polygon system includes numerous members like programmers, stakeholders, clients, etc. Developers rely on building their sidechains or scaling their applications using the Polygon SDK framework to deliver a great experience to their customers.
Why Choose Polygon?
Polygon is a project focused on solving flaws in the Ethereum network and the broader blockchain ecosystem.
Given the problem of slow block confirmations and high gas fees, Polygon wants to fix it by analyzing the communication between users and the decentralized system and making it simple and direct. How it’s done? With the help of a decentralized platform, which provides a solution for more permanent and extremely cheap transactions.
Polygon offers an optional, modular approach to ‘security as a service,’ offering one-click deployment of preconfigured blockchains and setting up an interoperable interface for exchanging random messages across blockchain networks.
All blockchains launched with Polygon have a security layer thanks to the MATIC PoS (Proof of Stake) chain, which is the Polygon main chain. Polygon PoS achieves staggering transaction speed and costs savings using sidechains for transaction processing.
While ensuring its longevity, Polygon also ensures Ethereum’s future with its integrated blockchain ecosystem.
How does Polygon Work?
There is a limited number of transactions that the Ethereum blockchain can perform within one second. On average is 17 transactions, Polygon can handle around 65,000 transactions per second. Every transaction on Ethereum comes with a cost, defined as a gas fee. The gas fee depends on network congestion at the time of the transaction and can reach up to $80. Therefore, Ethereum is entirely out of reach for most people since each transaction requires a one-time payment of more than $50. Is it cost-effective? For some, it isn’t.
How does Polygon help with this matter? Scaling systems like Polygon handle transactions on sidechains to save gas costs.
The overwhelming demand for developers prompted Polygon to include a blockchain bridge in its line of products. The PoS bridge enables developers to build dApps on the platform while gaining access to other platforms’ advantages.
Processing a series of transactions on the PoS blockchain neutralizes the need for Ethereum to process data independently. By grouping transactions from the main chain, Polygon makes Ethereum fast and light.
Is Polygon Unique?
There are various blockchain networks to choose from, but Polygon is the sole network that lets its token, MATIC, be staked on the Polygon blockchain. In return for staking, users can be compensated annually with interest payments after verifying transactions.
Polygon’s solution might be useful to small businesses, developers, and regular users. Its primary objective is to build an IoT (Internet of Things) on the Ethereum blockchain. IoT will enable internet-connected devices to transmit data to private blockchain networks to create tamper-proof records of shared transactions. The project intends to reach a billion Ethereum users without sacrificing decentralization or security.
Polygon is seen as a layer 2 solution, meaning that it represents a second layer built on top of the existing first layer (Ethereum) to improve the functionality of the first layer.
Polygon’s primary goal is to simplify quick blockchain transactions and scalability. It uses a custom version of the Plasma framework built on PoS checkpoints that run through the main Ethereum chain.
The term ‘Plasma’ refers to a framework that enables the development of child blockchains that rely on the main Ethereum chain as a stratum of arbitration and trust. Child chains in Plasma can be created to satisfy the needs of particular use cases, particularly those not yet feasible on Ethereum.
Thanks to this innovative technique, every sidechain on Polygon may score more than 65,000 transactions per block.
Polygon’s sidechains are structured to assist the various DeFi (decentralized finance) protocols accessible in the Ethereum ecosystem.
Certain elements make Polygon unique:
- ETH Compatibility
- Scalability
- Security
- Developer Experience
All these elements represent Polygon’s advantages and make it attractive to many users.
Build a Polygon dApp with Dev3
Building a Polygon decentralized app (dApp) isn’t rocket science. Remember, this process with a Dev3 app involves only two effortless steps.
Dev3 covers all EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) chains. EVM is software that executes smart contracts and evaluates Ethereum’s network state after each new block is added to the chain.
People develop for months just to connect to a particular chain, create and deploy a smart contract, etc. Here in Dev3, everything is simplified so that the whole process is a pleasure that inspires you to continue exploring the Dev3 app.
One way you can be convinced of our claims is related to the creation of Polygon dApp through our Dev3 platform.
The initial step involves logging into the Dev3 platform.
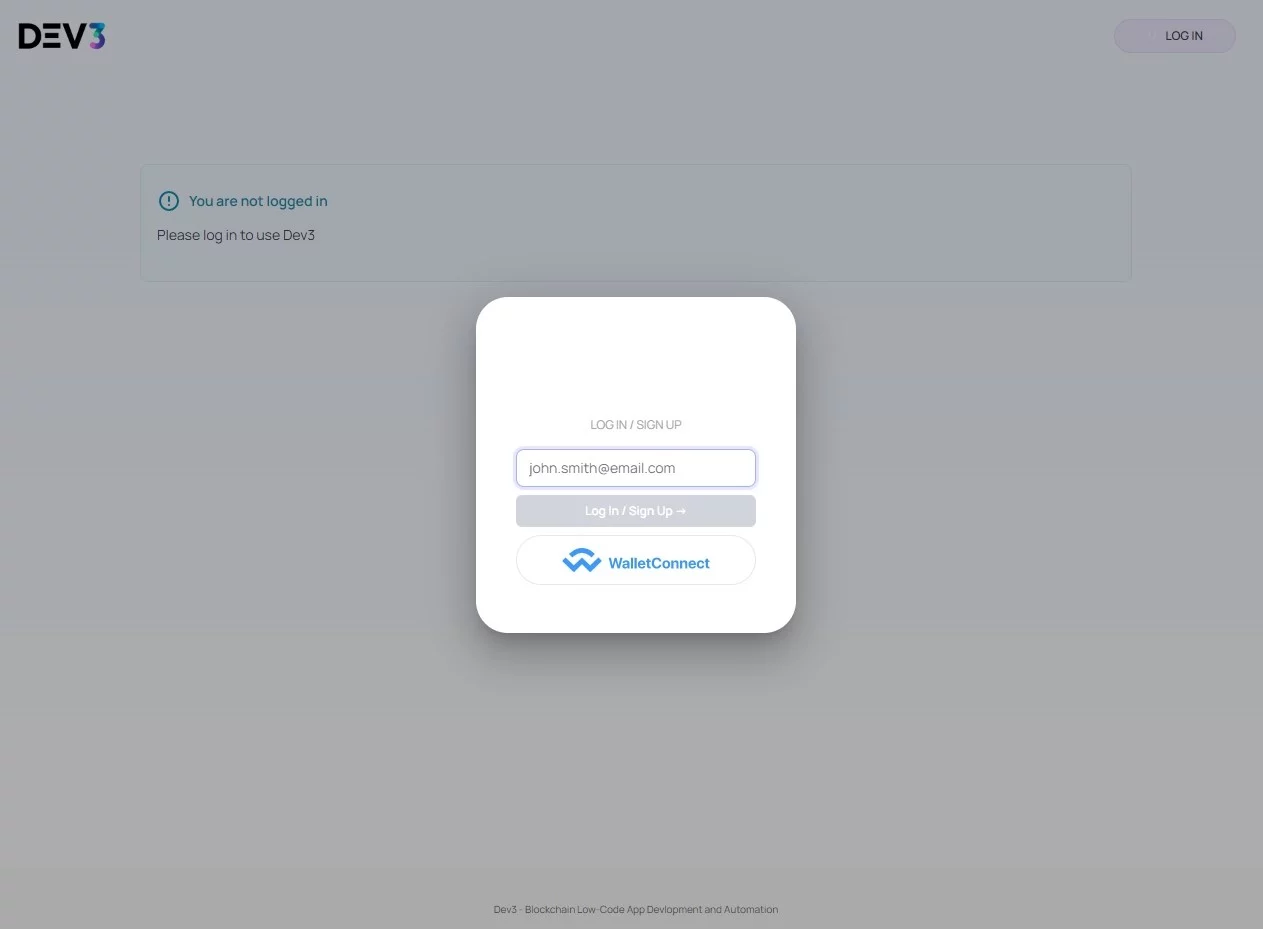
You have two options – connect your crypto wallet or log in with an email address. You must check your email and confirm your login if you decide to go with the second option. After this is complete, go back to your original browser tab.
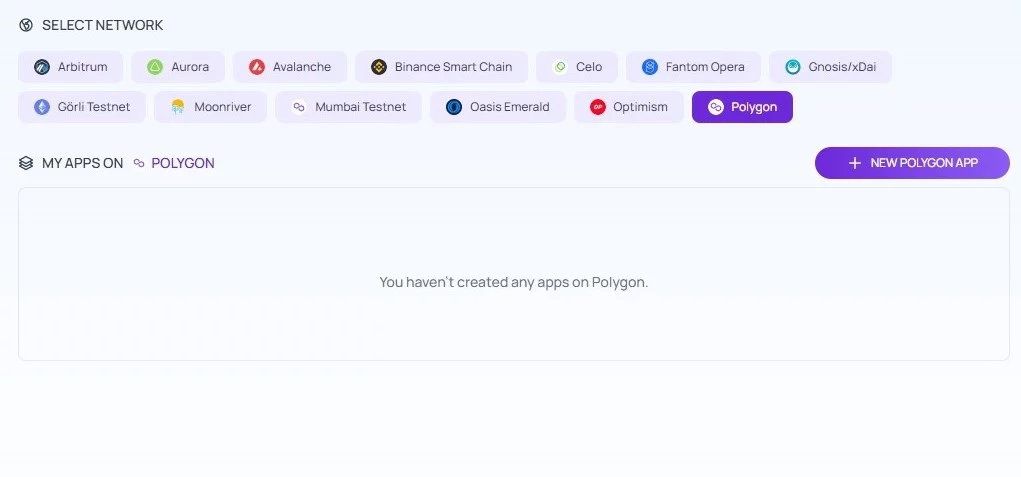
At the top of the interface, among all networks, pick Polygon. As you can see, no apps are created on the Polygon network. Therefore, you need to choose the ‘New Polygon App’ option.
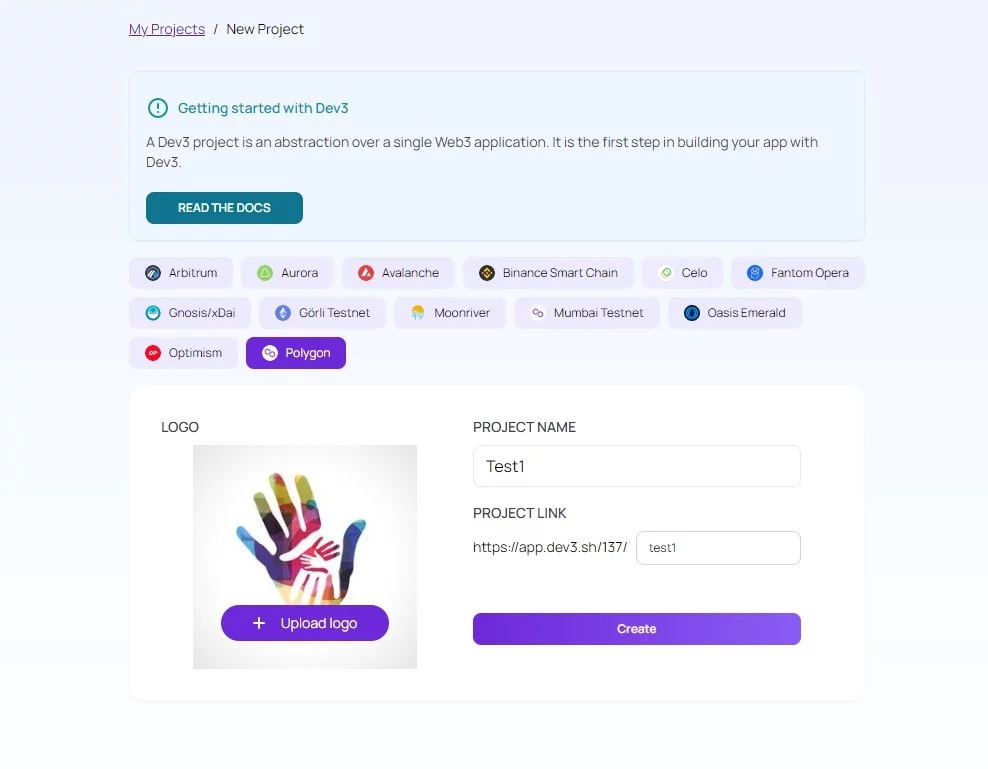
Upload a logo, choose a project name you feel it’s ideal for you, and click ‘Create.’ Wait for 10 seconds up to a few minutes to finish the process.
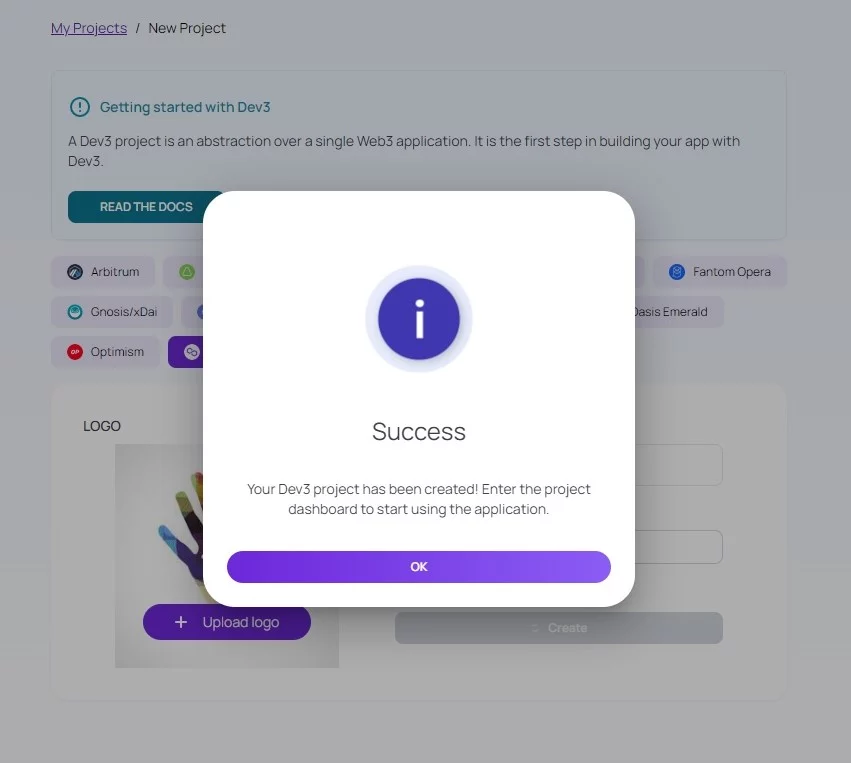
Voila! You’re done! It’s crazy how you can create a dApp in no time. You must be smiling from all the excitement. Now that the foremost step is completed, you are ready to continue using Dev3 platform.
Conclusion
Compared to its rivals, Polygon clearly distinguishes itself as a Layer 2 solution to be taken seriously. Although Polygon currently only supports the Ethereum blockchain, the network intends to expand support for additional blockchains based on community suggestions and consensus. It would make Polygon an interoperable decentralized Layer 2 blockchain platform.
